Phobias and Fear (50 Common Phobias List)
Practical Psychology
Phobias are what makes your hair stand on end, they may be what keep you up at night. Phobias can range from mild stressor to debilitating fear. Some just try to avoid their stressors and can handle it if they run into it.
However, there are those that are so severe that they cannot leave their homes or do certain things because of their fear that they will come into contact with their phobia.
What are Phobias?
Phobias are classified in the DSM-5 and recognized as a mental disorder and refer to a type of anxiety disorder characterized by the fear of a specific stressor. There are treatments and skills that you can learn to overcome these phobias and live as normally as possible.
50 Common Phobias List A-Z (And Their Meanings)
- Achluophobia - Fear of Darkness
- Aerophobia - Fear of Flying
- Agoraphobia - Fear of Open Spaces
- Arachnophobia - Fear of Spiders
- Apeirophobia - Fear of Infinity
- Aquaphobia - Fear of Drowning
- Athazagoraphobia - Fear of Being Forgotten
- Atychiphobia - Fear of Failing
- Barophobia - Fear of Gravity
- Bathophobia - Fear of the Deep
- Bibliophobia - Fear of Books
- Cacophobia - Fear of Ugliness
- Catoptrophobia - Fear of Mirrors
- Chromophobia - Fear of Colors
- Chronophobia - Fear of time
- Claustrophobia - Fear of Small Spaces
- Cleithrophobia - Fear of Being Trapped
- Coasterphobia - Fear of Roller Coasters
- Cynophobia - Fear of Dogs
- Dentophobia - Fear of Dentists
- Disposophobia - Fear of Getting Rid of Things
- Dystychiphobia - Fear of Accidents
- Enochlophobia - Fear of Crowds
- Equinophobia - Fear of Horses
- Ergophobia - Fear of Working
- Friggatriskaidekaphobia - Fear of Friday the 13th
- Galeophobia - Fear of Sharks
- Gamophobia - Fear of Marriage
- Gerascophobia - Fear of Getting Old
- Globophobia - Fear of Balloons
- Glossophobia - Fear of Speaking in Public
- Gynophobia - Fear of Women
- Hemophobia - Fear of Blood
- Hippopotomonstrosesquippedaliophobia - Fear of Long words
- Hydrophobia - Fear of Water
- Hypochondria - Fear of Illness
- Iatrophobia - Fear of Doctors
- Insectophobia - Fear of Insects
- Koinoniphobia - Fear of Crowds
- Lilapsophobia - Fear of Tornadoes/Hurricanes
- Lockiophobia - Fear of Childbirth
- Megalophobia - Fear of large things
- Metathesiophobia - Fear of Change
- Microphobia Fear of Small Things
- Monophobia - Fear of being Alone
- Mysophobia - Fear of Dirt and Germs
- Necrophobia - Fear of Death
- Nosocomephobia - Fear of Hospitals
- Nyctophobia - Fear of the Dark
- Obesophobia - Fear of Gaining Weight
- Ophidiophobia - Fear of Snakes
- Pantophobia - Fear of Everything
- Pathophobia - Fear of Disease
- Pediophobia - Fear of Dolls
- Pedophobia - Fear of Children
- Phasmophobia - Fear of Ghosts
- Philophobia - Fear of Love
- Phobophobia - Fear of Phobias
- Pyrophobia - Fear of Fire
- Scolionophobia - Fear of School
- Scopophobia - Fear of being Stared at
- Sociophobia - Fear of Judgement
- Somniphobia - Fear of Sleep
- Tachophobia - Fear of Speed
- Tonitrophobia - Fear of Thunder
- Trypophobia - Fear of Holes or Strange Patterns
- Venustraphobia - Fear of Beautiful Women
- Wiccaphobia - Fear of Witchcraft
- Xenophobia - Fear of Strangers or Foreigners
- Zoophobia - Fear of Animals
How do we Classify Phobias?
Leading minds in the world of psychology created the DSM (Diagnostic Statistical Manual) for a wide range of psychological disorders which also include Phobias.
This guide to diagnosing and explaining mental disorders classifies phobias under 5 different categories:
- Animal Phobias (Dogs, bears, rats, snakes)
- Natural Environment Phobias (mother nature; storms, the ocean, heights)
- Blood-Injection-Injury Phobias (seeing blood or watching it on television)
- Situational Phobias (closed spaces, trains, cars, planes)
- Other Phobias (avoidance of certain situations where harm to the self is possible but low)
These five categories encompass all of the phobias known to man, within each category there encompasses hundreds of phobias.

Animal Phobias
Animal phobias are probably the most common types of phobia out there. They can range from dogs to elephants; from rats to rhinos.
The onset of these phobias are typically from experiences in early life that lead to associated stress with the event.
For instance, if there is a dog barking ferociously as a young girl rides her bike down the sidewalk, she might get scared. If the dog comes up to her and knocks her off her bike and bites her, she may associate the trauma with dogs for the rest of her life, thus a phobia being born.
Animal phobias can also stem from scary stories that you hear. Some sources say that humans eat an average of eight spiders in their life while they sleep! After hearing that one may have an irrational fear that a spider would crawl into their mouth.
Other phobias may be there due to some of the species of animals being poisonous, an evolutionary advantage that has passed down throughout time. Indiana Jones has Ophidiophobia (the fear of snakes); This is likely due to the fact that some snakes are actually dangerous and can cause serious harm. However, the explorer doesn’t see a difference between venomous and non-venomous, he is scared of all of them the same.
Natural Environment Phobias
Natural environment phobias are fears of things that happen in nature. This could be bad weather or bodies of water. These phobias are common as well and associated with trauma or perceived danger.
If a person sees lightning strike a tree and catch it on fire and then hears thunder, under the right circumstances the phobia may be towards thunder in that case. The association was made with the sound, which in the mind of a person, could be the perceived cause of the fire.
Blood-Injection-Injury Phobias
Blood phobias are those associated with seeing blood in any form. The fear could be needles, or it could be open wounds. Psychologists believe this is another evolutionary advantage from the fear of getting hurt or seriously injured.
Some people have such strong fears of being hurt that they don’t want to leave their houses or safe spaces. There are people who have the irrational fear of their bodies falling apart, so they don’t take any risks and sadly, their lives revolve around that fear.
In other cases, some people suffer from “Glass Delusion”, a mental disorder that was first documented in the middle ages and people continue to suffer with today. This disorder makes people believe that they are made of glass, and therefore will shatter if they are not careful.
Situational Phobias
Situational phobias are those that are triggered by certain environments. This could be a plane ride, or it could be a crowded room. Any space that makes the person so anxious that they cannot handle it.
Many people have a more mild form of situational phobias that are diagnosed as social anxiety. Being in a room full of people or strangers throws these people into classic panic symptoms; Clammy hands, increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, dilated pupils, and feeling shaky.

Other Phobias
The phobias under this category are those where there is a possibility and a rational fear of harm, but that chance of harm has made the fear too great to handle. For instance, someone can be afraid of jumping off a diving board because they belly-flopped a few years before. A normal response is to avoid and maybe try again when it’s comfortable.
This can be exacerbated if someone develops a phobia after this experience. Not only would they not want to jump off the diving board at the pool anymore, but they may avoid pools and waterparks altogether.
Here are some funny phobias:

What Causes Phobias?
There is no one causes of phobias. Psychologists have linked some cases to:
- Genetics
- Traumatic experiences
- Learned responses
- Anxiety disorders and mental health conditions
- Physical health conditions
- Cultural factors
What happens Physically When Triggered by Phobia?
What happens in the body when a stressor that is related to the phobia is in sight is much like what happens to your body during the fight or flight response. In fact, the fight or flight response is many times triggered by the presence of the phobia.
The physical symptoms of being triggered by a phobia are:
- Dilated pupils
- Shaking
- Sweaty palms
- Chest pain
- Heart racing
- Difficulty breathing
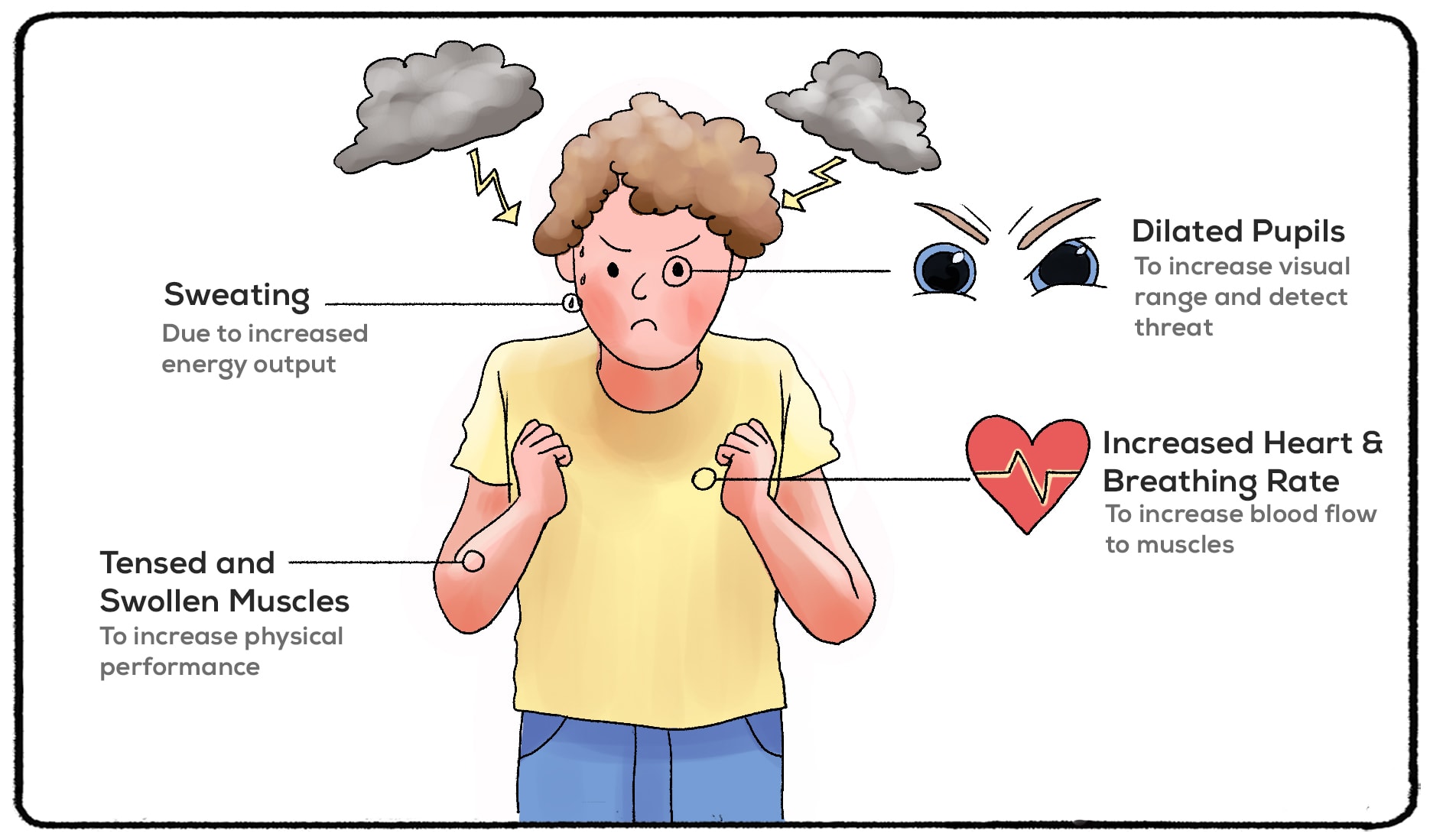
The response to a phobia is your body’s way of telling you to get yourself out of a situation that you have perceived as dangerous.
Some people will do anything to get out of the path of their phobias. For some people, they cannot contain themselves when presented with the phobia and will do anything to get themselves out, even if it means unintentionally hurting someone or themselves in the process.
Are Phobias Curable?
Phobias are treatable. They may not be completely curable in every case, but with treatment, phobias can become a livable condition. Even if you have an extreme or "strange" phobia, it's worth seeking out treatment and working toward living a productive life.
How Do You Face Your Fears or Treat a Phobia?
The best way to overcome a phobia is to present it to the afflicted in a safe environment. This would need to be done repeatedly and would show the person that there is no reason to be scared of their phobia. One of the best ways to replace bad memories is to drown them out with more pleasant ones.
Systematic Desensitization
If someone is afraid of the ocean because when they were little they got knocked off their surfboard and rolled with the current under a wave and that was the last time they ever went surfing, that bad memory will always be associated with that activity of surfing.
The best way to overcome that is to go out on the ocean with someone you trust, who makes you feel safe. The objective is to go when the conditions are the most safe. Don’t go to the beach on a windy and cloudy day to conquer your fear. Wait until it is bright and sunny, go out onto the water and just sit there.
Next time go out and maybe add an element that makes it more complicated, like riding a wave into the shore. Then the next time add to that, and so on. The best way to treat a phobia is to face it head on.
For extreme cases, systematic desensitization works very well. This means starting off by having a patient look at a picture of an ocean. Then moving on to watching a video of an ocean. With improvement, the patient could then be driven by an ocean a few times a day. With any luck, the patient will be much more likely to agree to actually visit the beach on a sunny day.
Medication
Sometimes the option to go and face the phobia isn’t there if the anxiety associated with the phobia is too severe to face the problem. Sometimes the best option is to start with an anti-anxiety medication.
This you will need to talk to your doctor or therapist about. Starting with treating the anxiety can prove to be helpful. Once you have the anxiety associated with the phobia under control you can move on to facing the phobia itself.
There is not one specific way to overcome a phobia, it can be tailored to the person and their specific needs. If you are interested in at-home remedies for phobias, check out our article on the Fight or Flight response.
